- SU’s technique rib fractures
- 发布于 2015-08-30 11:10 来源:苏志勇医生
Intrathoracic implantable fixation technique with SU’s bone plates and patent instruments using C- VATS for patients with rib fractures赤峰学院附属医院心胸外科苏志勇
Zhi Yong- Su Yi LEI -Zhang Tianshuo- Jiang Xin -Zhao
Chao-Wu Jingbo-Wu
Division of thoracic Surgery,Hospital Affiliated to Chifeng College,Chifeng,china
l corresponding author : Zhi Yong- Su
affiliation: Division of thoracic Surgery,Hospital Affiliated to Chifeng College,Chifeng,china
surface mailing address: Division of thoracic Surgery,Hospital Affiliated to Chifeng College,Chifeng,Inner Mongolia ,china ,postcode,(024001)
e-mail: suzhiyong1967@126.com
l Abstract
l Since 2009,In the experimental research foundation of animal, 3 cases patients with rib fractures have undergone surgical treatment using an intrathoracic implantable fixation technique under C- VATS with SU’s bone plates and patent instruments. We modified the different phases of the surgical technique using C-VATS, to control intercostal artery bleeding, to free up and identify the broken ends of the rib fracture, to pull open fractures off the broken ends of broken ribs, to properly align and fix the fracture, and to implant the Bone plate and Bone nail during the VATS. The results showed that the original technique was promising; however, long-term results are not available yet. This method is minimally invasive, leads to damage control and rapid rehabilitation.
l Introduction
l In recent years, internal fixation of fractured ribs, especially for flail chest, has received a lot of attention [ 1, 2, 3, 4]. Balci et al [5] found that patients with surgical internal fixation had significantly shorter ICU stays, In the late nineties, video-assisted thoracoscopy technology was applied by physician all over the world to many types of chest trauma [6,7,8], there are no reports on the technique of internal side fixation under C-VATS with bone plates in patients with rib fractures. we combined open surgery and thoracoscopy and designed a new surgical method and invented many types of patent equipment.
l Technique;
l 一 How to prevent and control the intercostal vascular hemorrhage
Figure 1
The patent instrument:
A prowling lead -wire -hook in Video assisted thoracoscopy(VATS )
Operation demo figure:
put absorbable suture line on lead hook during VATS
to prevent bleeding of the intercostal artery.
using the push device to knot in VATS
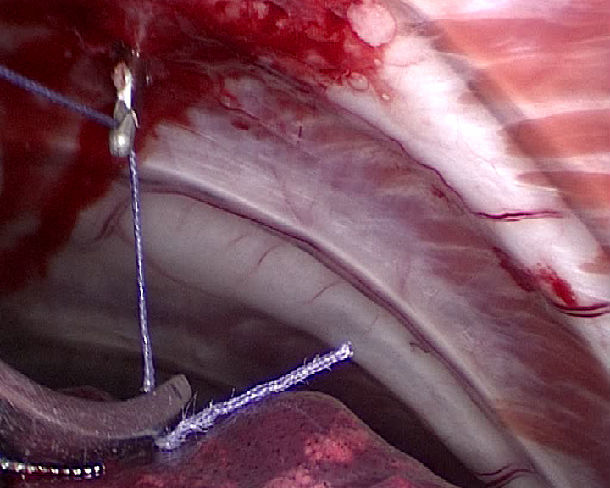
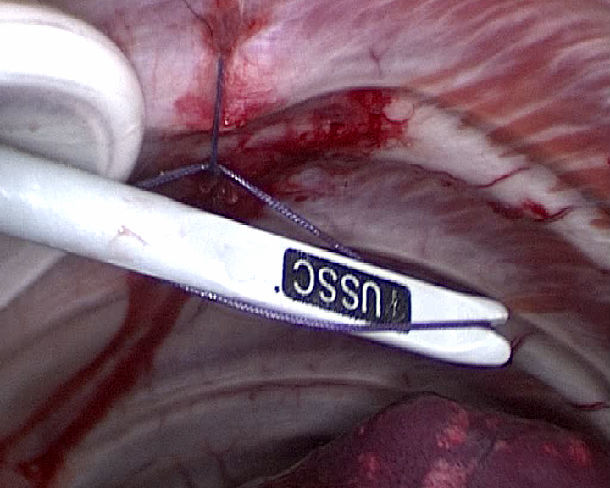
二 How to free two broken rib ends after intercostal vascular hemorrhage was controlled by knot during VATS
figure 2
The patent instrument: multi angle rib periosteal detacher and suction apparatus in VATS
This type of instrument can peel periosteum from the broken ribs under thoracoscopy, and it is a kind of suction apparatus. The stripping heads have different Angles and shapes,including cat ear,rectangular,and hemicyclic.
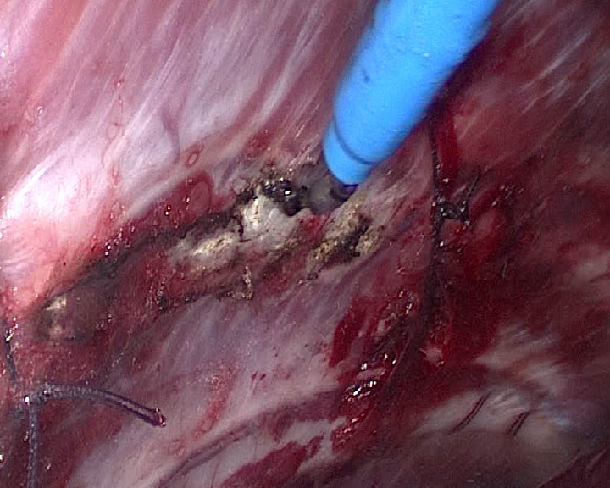
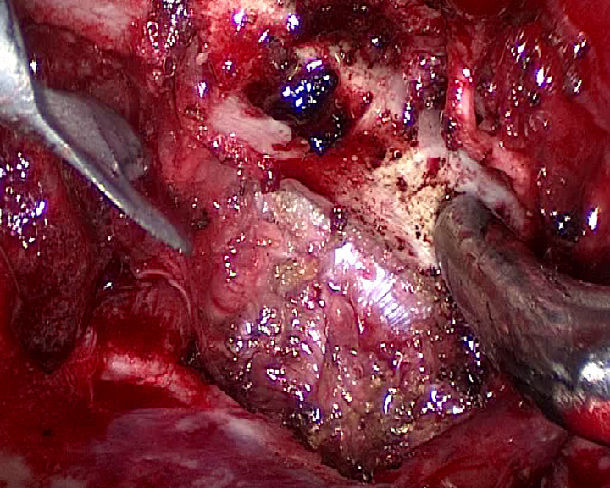
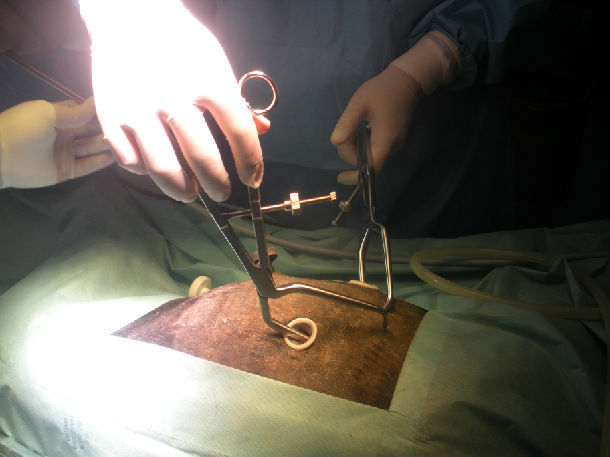
三How to pull open fractures off the broken ends of broken ribs
figure 3
The patent instrument: pulling- open forceps for broken ends of broken ribs duringVATS
figure 4
Surgical method:
Insert the lower teeth of the forceps into the chest and seize the inside portion of the rib 3 cm from the fracture end. The upper teeth penetrate into the outer side of the seized rib.
Operation demo figure
Pulling processes
Outside and inside view of the chest.
四 Fixed materials and methods:
1 Fixation with SU’s nickel titanium can memory alloy rib-connecting- plates in VATS,
figure 5
SU’s nickel titanium can memory alloy rib-connecting- plate:
Extend arm
Side view after hold
panoramic view of bone plate before penetrating
The patent instrument is Consists of the following parts:
hold arm, bone plate hole, hold arm hole, hold arm front is triangle pointed cone shape,hold arm hole stitching absorbable suture.
rib-connecting- plate becomes soft and easily molded at 0-4℃ .
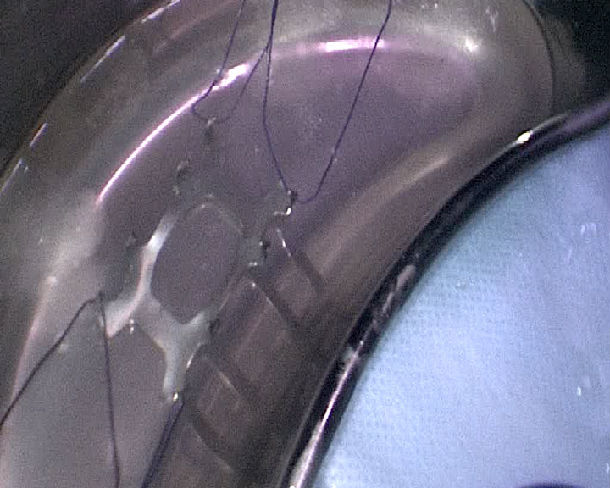

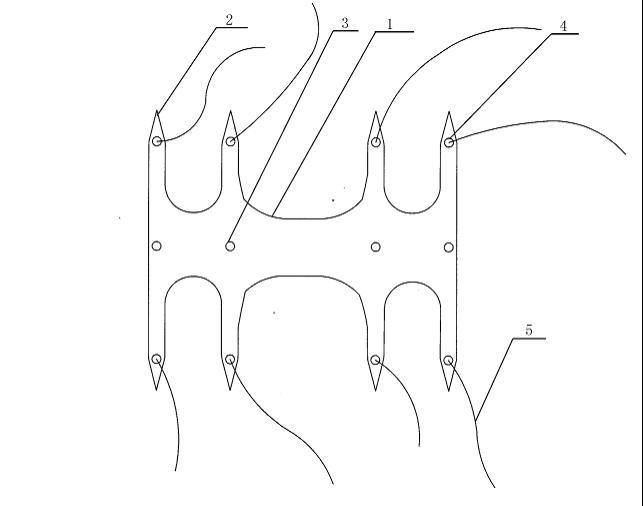
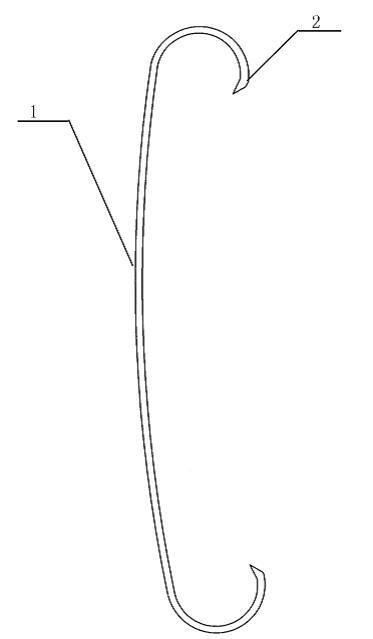
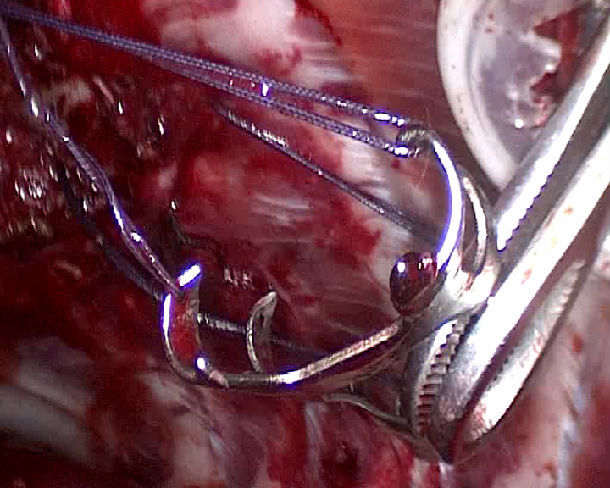
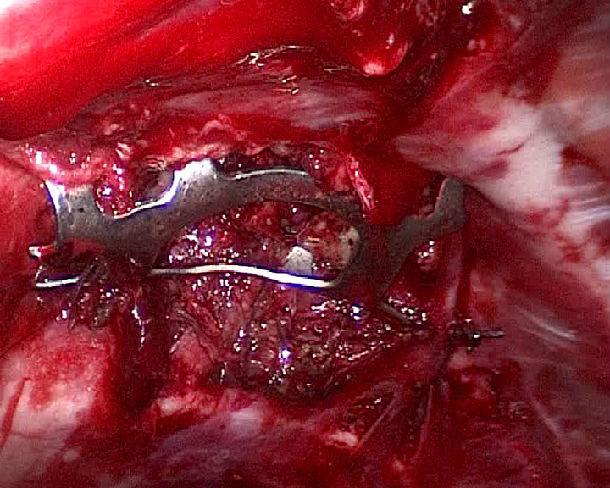
figure 6
How to implant the SU’s Nickel titanium can memory alloy rib-connecting- plate in C- VATS
Choose the suitable type of rib-connecting-plate according to x-ray and CT imaging. and place it into the specimen collecting bags with cold water and expanding hold arm with distraction device. Using the prowling lead-wire-hook during VATS, pull out the absorption line from the chest under thoracoscopic guidance. Adjust the angle using the multi-angle grasping forceps for bone nails and bone plates using c-VATS. Make the hold arm tips penetrate the upper and lower edges of the ribs. With increased body temperature, the memory alloy hold arm will restore to its original state and result in proper fixation of the fracture.
inner side of the fixated rib
From the chest interior surface to watch
2 Fixation with absorbable rib-connecting-pin
figure 7
multi-angle device used to drill marrow cavity of broken rib end during VATS
Surgical approach:
Pull the broken rib end open using the pulling-open forceps. Choose the appropriate multi-angle device to drill the marrow drill the marrow cavity of the broken rib end.
figure 8
Multi-angle grasping forceps for bone nails and bone plates in c-VATS.
Surgical approach:
Holding the bone nail with the multi-angle grasping forceps for bone nails and bone plates, insert it into the marrow cavity of the broken rib.
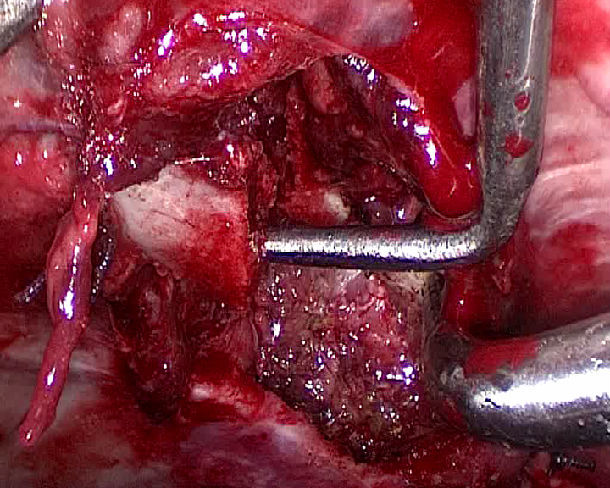

Comment
the indication for this technique are:
1 Especially suitable for single or multiple ribs fractures under the armpit, at the anterior chest wall or posterior chest wall.
2 Accompanied by injury to blood vessels and viscera that can be repaired in VATS.
3 Rib fractures of the axis type and island shape in areas suitable for fixation.
the contraindications for this technique are:
1. Severe complex trauma (tracheal rupture, important viscera,craniocerebral, abdominal, extremities, traumatic diaphragmatic hernia.)
2Injury to intrathoracic great vessels ,Inability to control chest cavity hemorrhage quickly.
3 Anatomical sites:
(1)rib fracture under the scapula
(2)Integration of a rib cartilage and near the spinal
(3)A high or low rib fracture: clavicle area, above the second rib, diaphragmatic area, fractures of ribs 11 and 12.
( 4) Close to the spine within 2 cm of the transverse process
Several principles for design incision:
(1) design incision according to fracture end position and possible intrathoracic viscera and vascular damage with comprehensive consideration of the incision distribution
(2) surgical hole and observational hole for the thoracoscope is best near a fracture end. This methods is convenient for fixation of fractures and decreasing surgical time.
(3) consider viscera the site of injury, convenient to repair hemostatic organ damage and convert to open surgery.
(4) Surgical hole can be 3-5 incisions.
Summary:
We designed a new method for different phases during VATS to control intercostal artery bleeding, free the broken ends of the rib fractures, pull the broken ends of the fracture together, align and fix them, and implant the bone nails and bone plates. The experimental results from surgeries on animals and some patients that our method is technically feasible. However, it cannot replace conventional open thoracic surgery for severe complex trauma. More experience is needed to improve the method and design better instruments to correct the shifting of fixed bone plates. In addition, we need to design surgical instruments for secondary removal and better incisional layout. Large sample cases determining the strength, recovery time, rehabilitation index, functional improvement, complication rates, and curative effects compared to open thoracic surgery are needed. This method is minimally invasive, conform to the damage control and rapid rehabilitation surgical philosophy.
